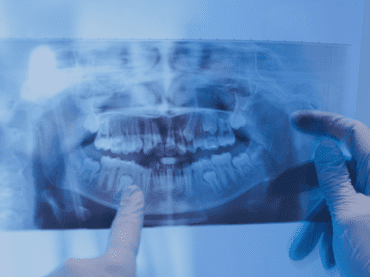
الأشعة السنية البانورامية
ما هي الأشعة السينية البانورامية؟
التصوير الشعاعي البانورامي، والذي يُطلق عليه أيضًا الأشعة السينية البانورامية، هو فحص بالأشعة السينية للأسنان ثنائي الأبعاد يلتقط الفم بأكمله في صورة واحدة، بما في ذلك الأسنان والفكين العلوي والسفلي والهياكل والأنسجة المحيطة.
الفك عبارة عن هيكل منحني يشبه حدوة الحصان. ومع ذلك، فإن الأشعة السينية البانورامية تنتج صورة مسطحة للهيكل المنحني. وعادة ما يقدم تفاصيل عن العظام والأسنان.
الأشعة السينية (التصوير الشعاعي) هي اختبار طبي غير جراحي يساعد الأطباء على تشخيص الحالات الطبية وعلاجها. يتضمن التصوير بالأشعة السينية تعريض جزء من الجسم لجرعة صغيرة من الإشعاع المؤين لإنتاج صور لداخل الجسم. الأشعة السينية هي أقدم أشكال التصوير الطبي وأكثرها استخدامًا.
على عكس الأشعة السينية التقليدية داخل الفم حيث يتم وضع كاشف الفيلم/الأشعة السينية داخل الفم، فإن الفيلم المخصص للأشعة السينية البانورامية موجود داخل الجهاز.
يتطلب هذا الاختبار القليل من التحضير الخاص أو لا يتطلب أي إعداد خاص. أخبر طبيبك إذا كان هناك احتمال أنك حامل. قم بإزالة أي مجوهرات أو نظارات أو أشياء معدنية قد تتداخل مع صور الأشعة السينية. سيُطلب منك ارتداء مئزر من الرصاص لحماية بقية جسمك من أي تعرض للإشعاع.
الأشعة السينية ثلاثية الأبعاد للأسنان (CBCT):
تعريف
توفر الأشعة السينية ثلاثية الأبعاد للأسنان، والمعروفة أيضًا باسم التصوير المقطعي المحوسب بالشعاع المخروطي (CBCT)، صورًا ثلاثية الأبعاد للأسنان وعظم الفك والهياكل المحيطة بها.
تكنولوجيا
يستخدم CBCT شعاعًا من الأشعة السينية على شكل مخروطي لالتقاط صور مفصلة من زوايا مختلفة، وإنشاء تمثيل ثلاثي الأبعاد لمنطقة الفم والوجه والفكين.
التطبيقات
تخطيط زراعة الأسنان: يستخدم CBCT على نطاق واسع للتخطيط الدقيق لوضع زراعة الأسنان من خلال تصور كثافة العظام وموقع الأعصاب والهياكل المجاورة.
تقييم تقويم الأسنان: يساعد في تقييمات تقويم الأسنان من خلال تقديم مناظر تفصيلية لعلاقات الأسنان والفك.
تحليل المفصل الفكي الصدغي: يمكن أن يساعد التصوير المقطعي المحوسب (CBCT) في تقييم حالات المفصل الفكي الصدغي (TMJ).
مزايا
دقة عالية: يوفر CBCT صورًا تفصيلية عالية الدقة لإجراء تشخيصات دقيقة.
التعرض المنخفض للإشعاع: أثناء العلاج بالإشعاع، يعرض العلاج المقطعي المحوسب (CBCT) المرضى عمومًا لجرعات أقل مقارنةً بالأشعة المقطعية الطبية التقليدية.
محددات
التكلفة: يمكن أن تكون أجهزة CBCT باهظة الثمن، مما قد يؤدي إلى ارتفاع التكاليف بالنسبة للمرضى.
لا يستخدم بشكل روتيني: بسبب المخاوف من الإشعاع، لا يتم استخدام CBCT بشكل روتيني في كل فحص للأسنان.
الأشعة السينية البانورامية للأسنان:
تعريف
تلتقط الأشعة السينية البانورامية رؤية واسعة للفم والفكين والأسنان بالكامل في صورة واحدة.
تكنولوجيا:
يقف المرضى أو يجلسون بينما تدور آلة الأشعة السينية حول رؤوسهم، مما يؤدي إلى إنشاء صورة ثنائية الأبعاد تشمل الفكين العلوي والسفلي.
التطبيقات:
نظرة عامة شاملة: تعتبر الأشعة السينية البانورامية ذات قيمة للحصول على نظرة عامة واسعة النطاق لهياكل الفم والوجه والفكين.
أداة التشخيص: تساعد في اكتشاف مشكلات مثل الأسنان المنطمرة واضطرابات الفك ومشاكل الجيوب الأنفية.
مزايا:
سريعة وبسيطة: يتم التقاط الأشعة السينية البانورامية بسرعة وتتضمن الحد الأدنى من حركة المريض.
الاستخدام الروتيني: يتم استخدامها بشكل شائع في فحوصات الأسنان الروتينية للتشخيص الأولي.
محددات:
تفاصيل محدودة: في حين أن الأشعة السينية البانورامية توفر رؤية واسعة، إلا أنها تفتقر إلى التفاصيل التي يوفرها CBCT.
غير مناسبة لحالات معينة: في بعض الحالات التي تتطلب تفاصيل دقيقة (مثل تخطيط الزرع)، قد تكون الأشعة السينية البانورامية غير كافية.